Cathodic Protection for Pipelines and Tanks: A Complete Guide to Preventing Corrosion
Protect your metal assets from rust and leaks—use cathodic protection to extend their life and reduce costs.
Corrosion is a natural process that damages metal when it reacts with moisture, soil, or water. This leads to rust, leaks, and expensive repairs. Cathodic protection for pipelines and tanks is a proven method to stop corrosion before it starts.
It works by turning the metal surface into a cathode, which prevents it from losing electrons. This stops rust from forming and keeps the structure safe and strong.
Table of Contents
Why Metals Corrode
Metals like steel are made from ores found in nature. When exposed to water or soil, they try to return to their original form—iron oxide (rust). This happens through an electrochemical reaction:
- Anode: Metal loses electrons and starts to corrode.
- Cathode: Metal gains electrons and stays protected.
Cathodic protection interrupts this process by supplying electrons to the metal surface.
How Cathodic Protection Works
Cathodic protection uses electrical current to stop corrosion. It makes the metal surface act like a cathode, where no rust forms. There are two main types:
1. Sacrificial Anode Cathodic Protection (SACP)
- Uses metals like zinc, magnesium, or aluminum.
- These anodes corrode instead of the protected structure.
- Simple to install and low maintenance.
- Best for small tanks, short pipelines, and low-risk areas.
2. Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP)
- Uses an external power source to push current.
- Anodes are made of durable materials like mixed metal oxide (MMO).
- Ideal for large pipelines, tank farms, marine structures, and complex networks.
- Can be monitored and controlled remotely.
Where Cathodic Protection is Used
Cathodic protection is widely used across industries to safeguard metal structures from corrosion, especially in harsh or moisture-prone environments.
This technique plays a vital role in extending the life of critical infrastructure by preventing electrochemical reactions that cause rust and degradation. Whether it’s buried pipelines, submerged marine assets, or reinforced concrete in humid zones, cathodic protection ensures long-term durability and safety. It is especially valuable in oil and gas, water treatment, marine engineering, and civil construction sectors.
Detailed Applications of Cathodic Protection:
1. Underground Pipelines

- Protects steel pipelines used for oil, gas, and water distribution.
- Prevents corrosion caused by soil moisture and stray currents.
- Often uses impressed current systems or sacrificial anodes.
2. Tank Bottoms
- Applied to above-ground and underground storage tanks.
- Anodes are placed beneath the tank to protect the bottom plate from soil-side corrosion.
- Essential for fuel, chemical, and water storage facilities.
3. Marine Structures
- Used on ship hulls, offshore platforms, piers, and jetties.
- Protects against saltwater corrosion and biofouling.
- Commonly uses zinc or aluminum sacrificial anodes.
4. Reinforced Concrete
- Protects steel rebars embedded in concrete from corrosion due to chloride ingress or carbonation.
- Used in bridges, parking structures, and coastal buildings.
- Can be retrofitted using embedded anodes and monitoring systems.
5. Well Casings and Piling
- Safeguards steel casings in oil, gas, and water wells.
- Prevents corrosion from groundwater and soil chemicals.
- Extends the operational life of deep foundations and offshore piles.
6. Internal Surfaces of Tanks and Vessels
- Applied inside water heaters, boilers, and chemical reactors.
- Sacrificial anodes are installed to protect internal metal surfaces.
- Especially useful in systems with aggressive fluids or high temperatures.
Soil and Water Conditions Matter
The effectiveness of cathodic protection depends on the resistivity of the surrounding soil or water:
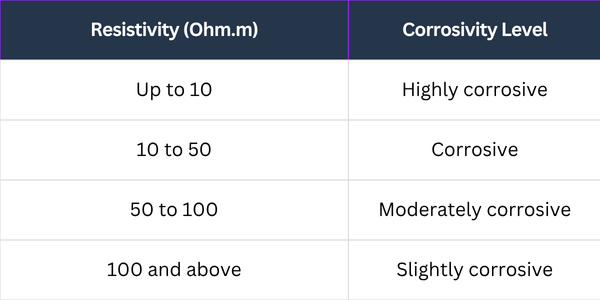
In highly corrosive environments, ICCP is usually preferred.
Designing a CP System: Key Points
A good cathodic protection system should include:
- Electrical continuity: All parts must be connected to ensure uniform current flow. This guarantees that every section of the pipeline or tank receives protection without leaving weak spots.
- Electrical isolation: Prevents current loss to nearby structures or foreign metallic objects. Isolation joints and insulating coatings help maintain efficiency and avoid interference with other systems.
- Monitoring tools: To check protection levels and adjust current as needed. Instruments like reference electrodes, test stations, and remote monitoring systems provide real-time data for reliable performance.
- Current calculation: Based on surface area, coating condition, and soil resistivity. Accurate calculations ensure the system delivers sufficient current, optimizing anode life and minimizing energy costs.
Tank Bottom Protection: Special Focus

Tank bottoms are highly vulnerable to corrosion due to continuous soil contact and moisture retention. Cathodic Protection for Pipelines and Tanks plays a critical role in extending service life and preventing costly failures.
- SACP may not protect the center of large tanks: Sacrificial anode systems often provide uneven current distribution, leaving central areas exposed. This limitation makes SACP more suitable for smaller tanks or localized protection zones.
- ICCP with linear anodes ensures even current across the tank bottom: By using impressed current systems, engineers can deliver controlled and uniform current density. Linear anodes are especially effective in covering wide surfaces, ensuring consistent protection even in large-diameter tanks.
- Anodes can be placed under the tank pad or around the perimeter: Strategic placement of anodes beneath the foundation or along the edges maximizes coverage. This design reduces shielding effects, enhances current flow, and ensures long-term corrosion prevention for the entire tank bottom.
Benefits of ICCP Systems
Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) systems are widely used in modern industries to safeguard critical infrastructure. They provide reliable corrosion prevention for large tanks and complex pipeline networks, making them a preferred choice where long-term durability and efficiency are essential. By integrating advanced monitoring and design features, ICCP ensures that Cathodic Protection for Pipelines and Tanks remains effective even in challenging environments.
- Long-lasting and low maintenance
- Remote monitoring and control
- Effective in high-resistivity soils
- Suitable for complex pipeline networks
- Deepwell groundbeds save space and reduce surface damage
Conclusion: Cathodic Protection for Pipelines and Tanks
Cathodic protection for pipelines and tanks is one of the most trusted methods to keep steel safe from corrosion. By applying this technique, industries can extend the life of their pipelines and storage tanks, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure safety in operations.
At Petromech Baroda LLP, we not only provide practical knowledge about cathodic protection but also help engineers and students to learn piping design and electrical design in easy steps. This combination of technical training and real‑world application makes learning more valuable and future‑ready.
