Ultimate Guide to Solar PV Systems: Design, Components & Benefits
Table of Contents
Introduction to Solar PV System
Solar PV system convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic panels. They are a clean, sustainable, and fast-growing solution for renewable energy.
Key Points:
- Solar energy is radiant light from the sun.
- PV panels convert sunlight into electricity.
- Solar PV is popular for homes, businesses, and remote areas.
What is Solar PV?
A Solar PV System is a setup that converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic panels. It’s a clean and reliable way to power homes, businesses, and even remote areas.
Key Points:
- Uses solar panels made of silicon cells.
- Converts DC power to AC for home use.
- Works with the electric grid or off-grid setups.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Solar PV
Solar PV system is eco-friendly and cost-effective, but they depend on sunlight and require space. Understanding both sides helps in making smart energy decisions.
Advantages:
- Clean and eco-friendly
- Low operating cost
- Works in remote areas
- Government subsidies available
Disadvantages:
- Efficiency ranges from 14–25%
- Depends on location and weather
- Land usage is high for large systems
Brief History of Solar Energy
Solar energy has come a long way—from early experiments with selenium to today’s advanced PV cells. Each milestone has pushed solar technology forward.
Highlights:
- 1876: Selenium generates electricity from sunlight.
- 1954: First PV cell created by Bell Labs.
- 2005: US adopts Investment Tax Credit for solar.
PV Array Components
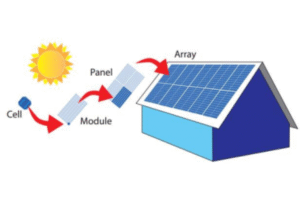
A solar array is made of cells, modules, panels, and arrays. These parts work together to capture sunlight and produce electricity efficiently.
Key Components:
- Cells → Modules → Panels → Arrays
- N-type and P-type silicon create electric fields
- Panels are sealed in glass/aluminum
PV System Components
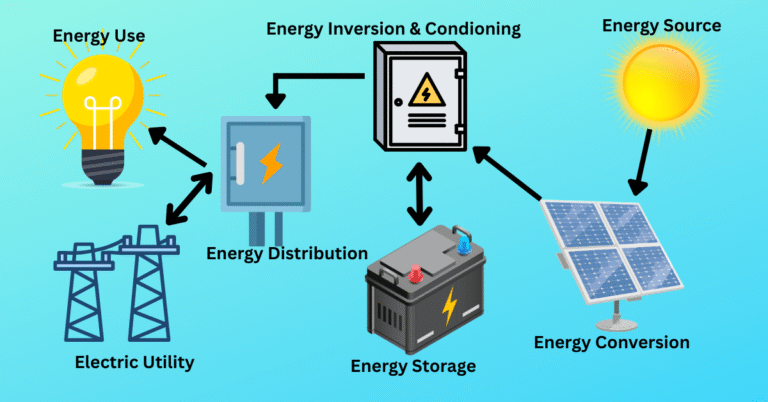
A complete solar PV system includes panels, inverters, mounting structures, and sometimes batteries. Each part plays a key role in energy conversion and delivery.
Components:
- Solar panels
- Inverter (DC to AC conversion)
- Mounting system
- Combiner boxes
- Battery storage (optional)
PV Cell Types
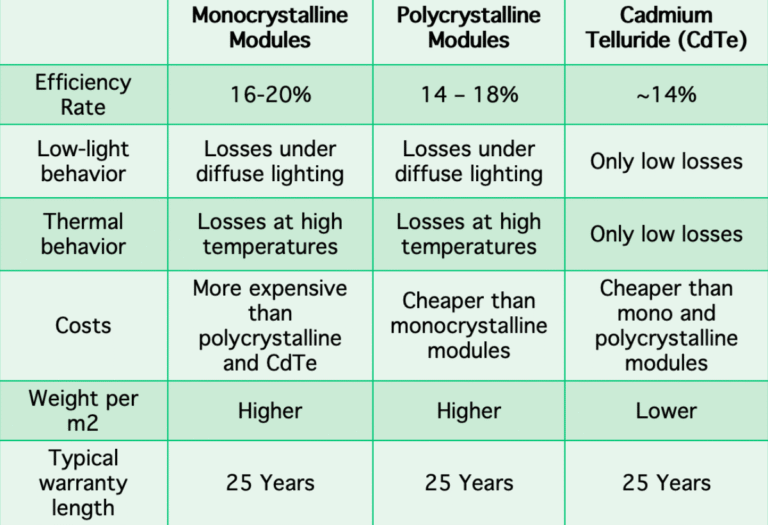
Solar cells come in different types like monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin film. Each has its own efficiency, cost, and ideal use case.
Inverter Types
Inverters change DC power from panels into AC power for use. Central and string inverters are common, and smart features help improve performance.
Types:
- Central Inverters (1–3 MW): Used in large systems
- String Inverters (10–100 KW): Ideal for smaller setups
- Features: MPPT, fault detection, reactive power control
Mounting Systems
Mounting systems hold solar panels in place—on rooftops, ground, or even water. The right mount improves energy capture and system durability.
Options:
- Ground Mount: Fixed tilt, single/dual axis trackers
- Rooftop: Sloped or flat roof systems
- Floating Solar: Installed on water bodies
- BIPV: Integrated into building surfaces

Engineering & Design Specifics
Solar design includes electrical, civil, structural, and mechanical planning. Good design ensures safety, performance, and long-term success.
- Grounding, protection, cable routing
- Lightning protection and arc flash analysis
Civil:
- Site grading, road design, stormwater management
Structural:
- Foundation design, roofing evaluation
Mechanical:
- HVAC and water systems for O&M buildings
Maintenance & Inspections
Regular checks keep solar systems running smoothly. Cleaning panels, inspecting wires, and testing inverters are part of a healthy maintenance routine.
Checklist:
- Clean and inspect panels
- Check wiring and connections
- Inverter and tracker tests
- Use infrared for hot spots
- Watch for corrosion and vegetation
Solar Design Tools
These tools help engineers design better solar systems. They offer layout planning, energy modeling, and financial analysis for smart decisions.
Xendee:
- Fast feasibility analysis
- Load profiles, utility rates, ROI
PVsyst:
- Energy modeling
- Performance ratio and layout optimization
SunDAT:
- AutoCAD layouts
- Rack specs and shading analysis
Microgrids and Solar Integration
Microgrids combine solar with other energy sources for flexible power. They work with or without the main grid and support energy independence.
Features:
- Can operate with or without the main grid
- Includes solar, wind, fuel cells, and storage
- Controlled via smart energy optimizers
Conclusion
Solar PV systems are a smart investment for clean energy. With the right design, components, and maintenance, they offer long-term benefits for homes, businesses, and communities.
